Understanding skin barrier function revolves around ceramides and lipids. Ceramides are essential lipids that keep your skin hydrated and resilient. They form a significant part of the stratum corneum, preventing water loss and protecting against irritants. An imbalance in ceramides can lead to skin dryness and conditions like atopic dermatitis. A healthy lipid composition, including cholesterol and fatty acids, is vital for barrier integrity. This balance helps maintain your skin's defense system. To grasp how these elements interplay and affect your skin, there's much more to uncover about their impacts and therapeutic applications.
Key Takeaways
- Ceramides are crucial lipids that maintain skin barrier function and prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL) in the stratum corneum.
- The stratum corneum's lipid matrix, primarily consisting of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids, is essential for protecting the skin.
- Ceramide deficiency is linked to skin dryness and disorders like atopic dermatitis, highlighting their importance for overall skin health.
- Environmental factors such as humidity and UV exposure can significantly affect ceramide levels, compromising skin barrier integrity.
- Tailored skincare formulations with ceramides can restore hydration and improve barrier function, especially during seasonal changes.
Overview of Ceramides
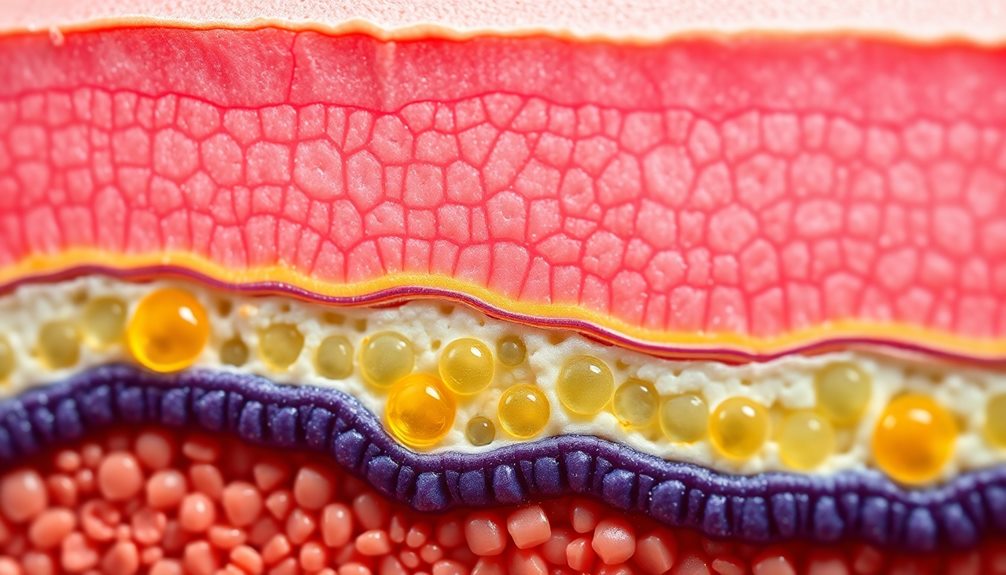
Ceramides, essential components of your skin's barrier, are lipids that consist of a sphingoid base and fatty acid. Primarily located in the stratum corneum, ceramides play an important role in maintaining skin barrier function. They help regulate lipid composition, which is critical for preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
When your skin's ceramide levels are balanced, it retains hydration effectively and stays resilient against environmental aggressors.
Ceramides are classified based on their fatty acid and sphingoid base types. Common examples include CER NP and CER AS, which contribute to the overall mass of ceramides in normal skin. Studies show that non-hydroxy ceramides make up about 55% of this mass, while α-hydroxy ceramides account for around 35%.
A deficiency in ceramides is often linked to dryness, while higher levels correlate with improved hydration and skin health.
Formulating effective skincare products with ceramides requires careful processing, as undissolved ceramides can hinder their ability to repair the skin barrier.
Structure of the Stratum Corneum
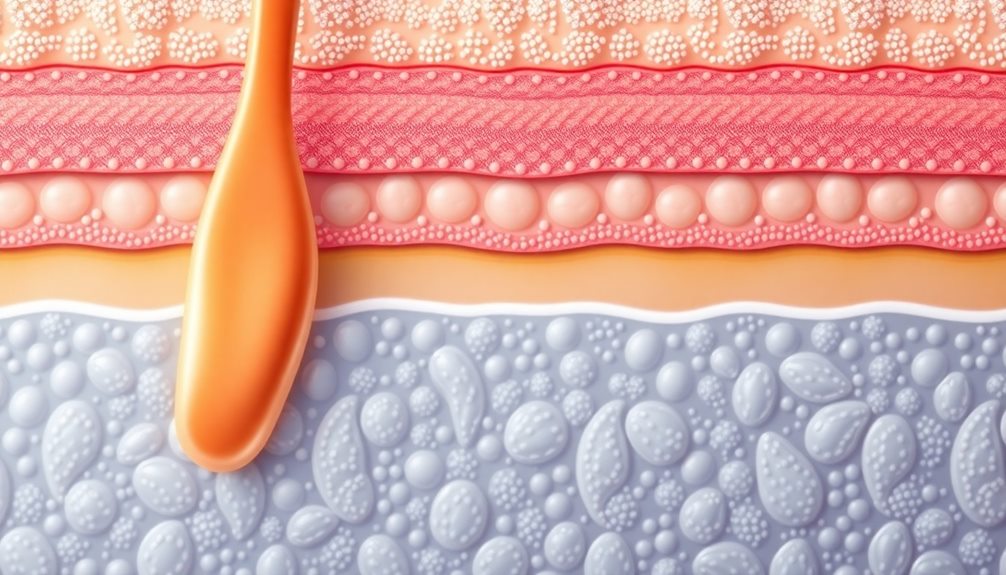
The stratum corneum (SC), often referred to as the skin's frontline defense, is vital for protecting your body from dehydration and environmental threats. This outermost layer of the epidermis is composed primarily of dead keratinocytes, called corneocytes, and intercellular lipids. Together, they form a significant barrier that maintains your skin's health and integrity.
Key aspects of the SC's structure include:
- Lipid Matrix Composition: The lipid matrix contains approximately 50% ceramides, 25% cholesterol, and 15% fatty acids, which play a notable role in barrier function.
- Lamellar Structure: Intercellular lipids in the SC are organized in a specific lamellar arrangement, featuring hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions that prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
- Impact on Skin Conditions: Changes in the lipid composition can lead to various skin conditions, with alterations in ceramide levels often correlating to impaired barrier function and increased skin irritability.
Understanding the structure of the stratum corneum helps you appreciate how vital its lipid matrix and ceramides are in maintaining an effective barrier against external threats.
Role of Ceramides in Skin Health
A significant component of the skin's lipid matrix, ceramides play an indispensable role in maintaining skin health. Making up about 50% of the skin's lipid composition, these molecules are essential for forming a multilamellar barrier that prevents transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and shields your skin from environmental aggressors.
The stratum corneum contains various classes of ceramides, with non-hydroxy ceramides being the most prevalent.
When ceramide levels are low, you might experience dryness and irritation. Conversely, higher ceramide levels are linked to improved hydration and reduced TEWL, enhancing your overall skin health.
Ceramides also contribute to important cell signaling processes, influencing skin cell apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation, all significant for a healthy complexion.
Impaired ceramide synthesis can lead to skin barrier dysfunction, commonly seen in conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. This connection underscores the therapeutic potential of ceramide-based treatments.
By incorporating ceramides into your skincare routine, you can support your skin barrier, improve hydration, and promote resilience against dryness and irritation.
Prioritizing ceramides ultimately fosters healthier, more vibrant skin.
Ceramide Classification and Types
Understanding the different classifications of ceramides is essential for optimizing skin health. Ceramides play an important role in maintaining skin barrier integrity, and knowing their types can help you choose the right skincare products.
Here's a quick overview of the main ceramide classifications:
- Non-hydroxy ceramides (CER NP): These are formed with non-hydroxy fatty acids and phytosphingosine, making up about 55% of total ceramide mass in the stratum corneum.
- α-hydroxy ceramides (CER AS): Comprising around 35% of ceramide content, these are made with α-hydroxy fatty acids and sphingosine, contributing to hydration.
- ω-esterified ceramides: Accounting for about 10%, these ceramides enhance lipid composition and overall skin health.
The specific acyl chain length of these ceramides greatly affects their functionality in skincare formulations.
Variations in ceramide composition can also be influenced by environmental factors, with low levels often linked to skin conditions like dryness and atopic dermatitis.
Skin Barrier Function Mechanisms

Understanding how ceramides and lipid composition work together is essential for maintaining your skin barrier.
Ceramides not only hydrate your skin but also prevent water loss, while the overall lipid arrangement plays a significant role in barrier integrity.
Role of Ceramides
Ceramides play a significant role in maintaining skin barrier function, acting as key building blocks that hold everything together. Constituting about 50% of the total lipid composition in the stratum corneum, they form a multilamellar structure that enhances hydration and protects against transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
Understanding the role of ceramides in skin health can be summarized in three important points:
- Barrier Integrity: Ceramides facilitate the formation of the skin barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering and retaining moisture.
- Hydration: By maintaining proper hydration levels, ceramides help keep your skin smooth and plump, combating dryness and irritation.
- Signaling Functions: Acting as signaling molecules, ceramides influence essential processes like apoptosis, cell proliferation, and differentiation, further contributing to overall skin health.
Low levels of specific ceramides, like ceramide 3, can lead to increased TEWL and skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis.
Lipid Composition Importance
Often overlooked, the lipid composition of the stratum corneum is fundamental for maintaining skin barrier function. This outermost skin layer is rich in ceramides, cholesterol, and free fatty acids, ideally in a balanced ratio of 1:1:1. This balance is critical for preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and protecting against external irritants.
Ceramides, which account for about 50% of the lipid composition, play a central role in forming a multilamellar structure that safeguards against dehydration. Research shows that reduced levels of specific ceramides, particularly ceramide 3, correlate with increased TEWL and various skin conditions like atopic dermatitis. This highlights how essential ceramides are for overall skin health.
Furthermore, the lipid organization within the stratum corneum features both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, creating lamellar structures that enhance barrier function against environmental challenges.
Seasonal variations affect lipid composition, with studies revealing decreased ceramide levels during the dry winter months. This underscores the necessity for tailored skincare formulations to support barrier function throughout the year, ensuring your skin remains healthy and well-protected.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Your skin barrier function is directly affected by environmental factors like humidity and temperature.
During dry winter months, you might notice increased water loss and lower lipid levels, which can compromise your skin's integrity.
Meanwhile, UV exposure can actually boost certain lipids, highlighting the complex relationship between your skin and its environment.
Seasonal Lipid Variations
Seasonal changes can dramatically influence skin barrier function, particularly during winter when lipid levels typically drop.
This reduction can lead to increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), leaving your skin more vulnerable to dryness and irritation. Understanding how seasonal variations affect your skin is vital for maintaining its health.
Here are three key impacts of winter on your skin barrier:
- Decreased Lipid Levels: Cold weather often results in reduced ceramide synthesis and a decline in the lipid composition of your skin, which are essential for maintaining hydration.
- Heightened Sensitivity: With lower ceramide levels, your skin barrier becomes impaired, making it more sensitive to environmental irritants and leading to discomfort.
- Increased TEWL: The harsh winter conditions can disrupt your skin's natural barrier, causing it to lose moisture faster, which contributes to a rougher texture and a feeling of tightness.
To combat these effects, consider adapting your skincare regimen by incorporating products with higher concentrations of ceramides and occlusive agents.
This will help restore hydration and support ideal skin barrier function during those colder months.
UV Exposure Effects
UV exposure greatly impacts skin barrier function, leading to a cascade of changes that can compromise your skin's health. When you're exposed to UV rays, the levels of ceramides in your stratum corneum can decrease, weakening your skin barrier. This results in increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), making it harder for your skin to stay hydrated.
Chronic UV exposure disrupts lipid organization, allowing harmful substances to penetrate your skin more easily. The relationship between UV exposure and skin lipids is complex. While UV therapy can sometimes increase levels of major skin lipids, the overall effects often contribute to the aging process. Increased skin pH and decreased lipids exacerbate this issue, impairing your skin barrier integrity further.
To combat these negative effects, incorporating protective skincare products enriched with ceramides is essential. These formulations can help restore lipid organization and improve your skin barrier function, ultimately reducing the adverse impacts of UV exposure.
Prioritizing protective skincare won't only help maintain hydration but also support your skin's resilience against environmental stressors.
Humidity and Barrier Integrity
Humidity plays an essential role in maintaining skin barrier integrity, and it can be a game-changer for your skin's health. When humidity levels drop, your skin can experience increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), leading to a compromised barrier. This is especially common during dry winter months when ceramide and lipid levels decrease, making your skin more susceptible to irritation and dryness.
Here's how humidity affects your skin:
- Low Humidity: Leads to reduced lipid organization in the stratum corneum, impairing barrier integrity.
- Optimal Humidity: Enhances hydration, promoting better lipid synthesis and healthier skin.
- Fluctuating Conditions: Extreme temperatures can disrupt ceramide profiles, increasing vulnerability to conditions like atopic dermatitis.
To preserve your skin's barrier integrity, aim for balanced humidity levels. When the environment is too dry, consider using a humidifier to restore moisture.
This helps maintain your skin's natural lipids and ceramides, ensuring your barrier remains strong and resilient. By understanding the impact of humidity, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your skin's health.
Ceramides in Skin Disorders
Ceramides play an essential role in maintaining the skin's barrier function, and low levels can lead to serious skin disorders. When your skin's ceramide levels are reduced, it becomes more vulnerable to transepidermal water loss (TEWL), which can exacerbate conditions like atopic dermatitis.
Studies show that individuals with atopic dermatitis often have considerably lower levels of ceramides 1 and 3, negatively impacting their skin hydration and barrier integrity.
Additionally, compromised ceramide biosynthesis is common in various skin disorders. For instance, mutations in the filaggrin gene can further deplete ceramide levels, resulting in an impaired skin barrier.
This deficiency not only affects hydration but also increases susceptibility to irritants and allergens.
Fortunately, topical applications of ceramides have been shown to help restore damaged lipid layers. By enhancing barrier repair and hydration, these treatments can considerably improve skin conditions.
Research indicates that boosting ceramide levels in skincare formulations can provide therapeutic benefits for a range of skin disorders, including psoriasis and eczema.
Formulation Challenges in Skincare

Creating effective skincare products presents unique formulation challenges, especially when it comes to integrating ceramides. To guarantee that ceramides effectively enhance the skin barrier, you need to address several key factors during formulation:
- Processing Techniques: High-temperature heating is often necessary to properly dissolve ceramides, allowing for their effective integration into your skincare products.
- Ceramide Class and Acyl Chain Length: Consideration of the specific ceramide class and acyl chain length is essential. This can notably impact the lipid structure and the overall benefits for skin barrier repair.
- Seasonal Adaptation: Recognize that seasonal variations, like increased transepidermal water loss during winter, might require tailored ceramide-rich formulations to maintain skin barrier integrity year-round.
If ceramides remain undissolved in your formulations, they can compromise the efficacy of skin barrier repair.
Disorganization in lipid structure can lead to diminished barrier integrity, resulting in increased skin sensitivity. By carefully maneuvering these formulation challenges, you can create skincare products that not only deliver ceramides effectively but also support the health and resilience of the skin barrier.
Therapeutic Applications of Ceramides

When you incorporate ceramides into your skincare routine, you enhance hydration and support your skin's barrier repair mechanisms.
These lipids not only help lock in moisture but also strengthen the skin’s defense against irritants. In addition to their moisturizing properties, these lipids also play a crucial role in maintaining the skin’s barrier function, making it less susceptible to environmental stressors. Furthermore, they can be used in hair care products, serving as a styling wax for better hold. This versatile ingredient makes it an essential component of skincare and haircare formulations.
Understanding how ceramides function can transform your approach to maintaining healthy, resilient skin.
Ceramide-Enhanced Hydration
The skin's ability to retain moisture and protect against environmental irritants relies heavily on the presence of ceramides, which make up about 50% of the lipids in the stratum corneum.
These important components play a significant role in enhancing skin hydration and preventing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). If your skin often feels dry or irritated, incorporating ceramide-based products can make a considerable difference.
Here are three key benefits of ceramide-enhanced hydration:
- Improved Barrier Function: Ceramides help restore lipid layers, strengthening your skin's defense against environmental aggressors.
- Effective Moisture Retention: By locking in moisture, ceramides combat dryness, especially during harsh winter months.
- Skin Condition Relief: Topical ceramide formulations have been clinically proven to alleviate symptoms of conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
With low levels of ceramides linked to increased skin irritation and dryness, it's evident how indispensable they're for maintaining skin health.
Barrier Repair Mechanisms
Many people underestimate the significance of ceramides in skin barrier repair, yet these lipids play a vital role in restoring and maintaining skin integrity.
Ceramides are necessary for forming and sustaining the lipid layers of your skin barrier, which helps retain hydration and reduce transepidermal water loss (TEWL). When your skin barrier is compromised, it can lead to dryness and irritation, conditions often linked to lower ceramide levels. Incorporating natural alternatives, such as herbal remedies, can further enhance the skin's hydration and elasticity, complementing the benefits of ceramides.
Topical formulations containing ceramides have proven effective in restructuring damaged lipid layers, making them a go-to for treating skin conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
By incorporating these formulations into your skincare routine, you can enhance skin health and strengthen your skin barrier's defenses.
It's important to note that the proper formulation of ceramides is essential for their effectiveness. Specific processing techniques guarantee they remain dissolved and can perform at their best.
Additionally, seasonal variations can influence ceramide levels, highlighting the need for tailored ceramide-based treatments to adapt to environmental changes.
Future Directions in Research

Exploring the future of skin barrier research reveals exciting opportunities to enhance our understanding of ceramides and their critical role in skin health. As you immerse yourself in this field, consider focusing on the following areas:
- Ceramide Classes: Investigate the precise roles of different ceramide classes and their fatty acid compositions in maintaining skin barrier integrity and functionality.
- Environmental Factors: Examine how environmental factors influence ceramide synthesis and organization, shedding light on seasonal variations in skin barrier function and hydration levels.
- Advanced Formulations: Develop advanced formulation techniques to guarantee peak integration of ceramides in skincare products, enhancing their therapeutic efficacy for skin barrier disorders.
Future research should also explore the genetic regulation of ceramide biosynthesis pathways, which can help identify potential biomarkers for skin diseases like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Additionally, understanding the interactions between ceramides and other lipids in the lipid matrix will deepen your insights into their implications for overall skin health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Science Behind the Skin Barrier?
The skin barrier's science revolves around its structure, which protects you from moisture loss and environmental factors. It consists of cells and lipids that work together, ensuring your skin stays hydrated and healthy.
What Is the Science Behind Ceramides?
Imagine ceramides as the unsung heroes of your skin, weaving a protective tapestry. They help retain moisture, combat irritation, and signal cellular health. Understanding them is key to revealing your skin's natural radiance and resilience.
What Is the Function of the Skin Lipid Barrier?
The skin lipid barrier protects your skin by preventing moisture loss and shielding against environmental irritants. It maintains hydration, ensuring your skin feels smooth and healthy while minimizing the risk of dryness and irritation.
What Is the Difference Between Lipids and Ceramides?
Lipids are a broad group of organic molecules, while ceramides are specific lipids made of sphingoid bases and fatty acids. Ceramides play an essential role in skin barrier function and moisture retention, unlike other lipids.
Conclusion
In the garden of your skin, ceramides serve as the sturdy fence that keeps out intruders while nurturing the delicate blooms within. By understanding their essential role in maintaining the skin's barrier, you can cultivate a healthier complexion. With ongoing research, these unsung heroes may soon reveal even more secrets, helping you protect and enhance your skin's beauty. So, as you tend to your skincare routine, remember the power of ceramides in this vibrant ecosystem.